Performing a Microsoft CA Database cleanup is a fairly simple task that every PKI administrator should complete regularly. Why, you ask. Well, there is no point in keeping expired certificates around as they no longer serve a purpose. Doh! Believe it or not, failed and stale pending certificate requests can also be removed from the database. Without further ado, let’s get right into how to easily perform a Micorosft CA database cleanup.
QuickSteps – Microsoft CA Database Cleanup
Run the following CERTUTIL commands in Windows PowerShell or Command Prompt to clean up the CA database:
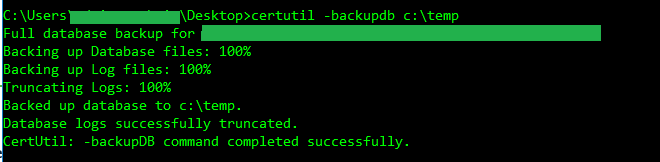
certutil –backupdb c:\temp
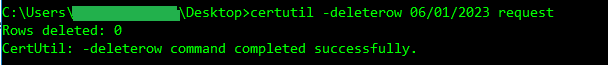
certutil -deleterow mm/dd/yyyy request
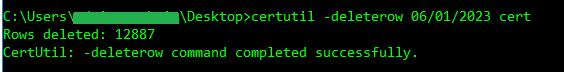
certutil -deleterow mm/dd/yyyy cert
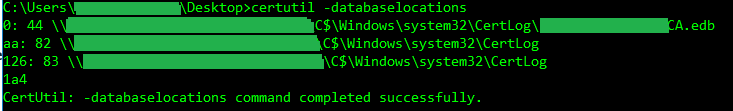
certutil -databaselocations
net stop certsvc
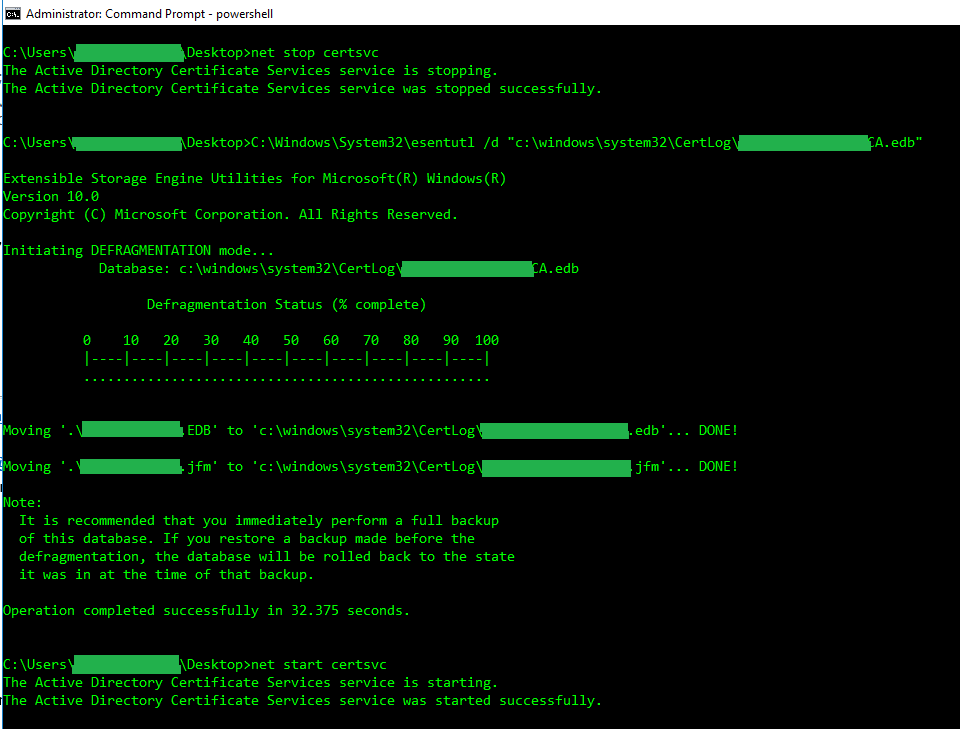
C:\Windows\System32\esentutl /d "FULL-PATH-TO-EDB-FILE”
net start certsvc- Please note that for larger databases the deleterow command can take hours or even days to complete. If it is taking a while, simply walk away and check again at a later time.
- mm/dd/yyyy refers to the certificate expiration date, not the effective date. This should be some date in the past! Do not delete certificates that are still valid. For request records in the database (not certificates), the date refers to the submission date of the certificate request. The command will remove all requests submitted on or before the specified date.
- FULL-PATH-TO-EDB-FILE refers to the database (.edb) file location and name. For example, c:\windows\system32\CertLog\CAServerName.edb, where CAServerName is the name of the Certification Authority. To find this path simply run the command
certutil -databaselocations.
About the Microsoft CA Database
A Microsoft CA stores information about its certificates, requests and published templates in what is called an Extensible Storage Engine (ESE) Database File (EDB), also known as JET Blue. This file is usually located in the C:\Windows\System32\CertLog directory and is named CAServerName.edb where CAServerName is the name of the Certification Authority.
In order to view the contents of this database file on a Microsoft CA server we would open a Certification Authority snap-in by running the certsrv.msc command or via MMC Console (mmc.msc).
The database (.edb) file can get quite large in some PKI environments and should, hence, be regularly maintained.
Microsoft CA Database Cleanup Procedure
Step 1 – Perform a database backup
certutil –backupdb c:\tempStep 2 – Delete failed and pending requests
certutil -deleterow mm/dd/yyyy requestStep 3 – Delete expired certificates
certutil -deleterow mm/dd/yyyy certStep 4 – Find database location
certutil -databaselocationsStep 5 – Compact the database
Note: The Active Directory Certificate Services (CertSvc) service must be stopped before running the esentutl command and then re-started after defragmentation completes.
net stop certsvc
C:\Windows\System32\esentutl /d "FULL-PATH-TO-EDB-FILE”
net start certsvcStep 6 – Verify database size was reduced
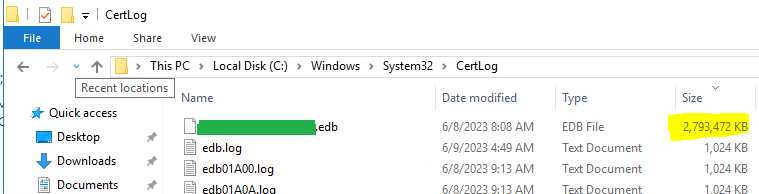
Microsoft CA Database Cleanup – Before
Microsoft CA Database Cleanup – After
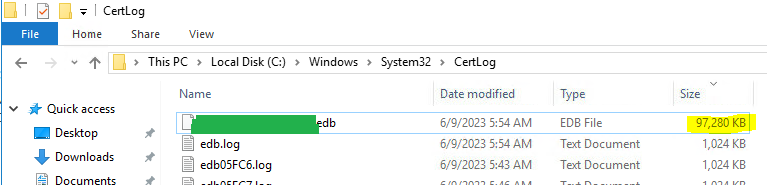
Now that we have cleaned up the database, our CA database file size went from a whopping 2.7GB to a mere 97MB. What were your BEFORE and AFTER database (.edb) file sizes? Share by posting a comment below! ↓
9 thoughts on “Microsoft CA Database Cleanup”
Excellent guide for Microsoft CA Database Cleanup.
Thank you very much for sharing. It helped me understand the cleanup process.
Thanks! Straightforward and direct instructions. Disk size did seem to increase after deleting some expired certs.
Thanks for the guide….
I am running into an issue which i am talking about on reddit here – https://www.reddit.com/r/sysadmin/comments/1cp5478/cleaning_up_ca_seems_to_have_hung_anyone_have/
Basically the command “certutil -deleterow mm/dd/yyyy request” is hanging and the CPU used by certsvc.exe goes to 100%.
My gut feel is that there is a corrupt record or similar that is getting the process stuck into a loop. Have you seen that before? or have any suggestions on what i can do to get around it ?
Hi Ben. We’ve seen certutil -deleterow run upwards of 3 days. We’d normally just walk away and let it do its thing. We’ve on several occasions also just hit CTRL+c to stop it and then kick it off at a later, more convenient, time. Best is to just let it run as long as it needs to complete. Maybe kick it off on a Friday evening or during off hours to allow it to complete. From our experience, in each case, it always eventually completes.
Great guide, very clear and well explained.
“mm/dd/yyyy refers to the certificate expiration date up to which to delete database records (submission date for requests)”
The above confuses. The date is expiry date only not effective date.
Thank you. Updated for better clarity.
Hi, great guide. What about scenarios where we have a root and intermediate CA server? Do you just run these steps on both?
Hi Andrew – thank you! 😊
Yes, you can absolutely run these steps on any type of Microsoft CA. In most cases, the root CA tends to have less data in its database, since it usually doesn’t issue as many certificates as an intermediate CA. So there might not be a lot to clean up there.
That said, it’s always a good idea to double check. You can do that by checking the size of the .edb file for the root CA – it’s likely located at C:\Windows\System32\CertLog\.
Hope that helps!